Kidney and bladder ultrasound | Republikas laukuma klīnika
Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder is a painless and safe diagnostic method that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of these organs’ structure and condition.
USG of the kidneys and bladder is an effective way to quickly detect kidney stones, tumors, infections, or other pathologies. The procedure typically lasts 15–30 minutes, and patients can return to their daily activities immediately afterward.
At “Republikas laukuma klīnikā”, highly qualified specialists perform kidney and bladder ultrasounds in a comfortable manner to diagnose various urinary system problems. Timely diagnostics can prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes.

Dr. Vladimirs Šalajevs

Dr. Alma Egle

Dr. Jeļena Dubinčaka
Kidney ultrasound (USG)
Kidney ultrasound is a medical imaging procedure that uses sound waves to create images of the internal structure of the kidneys. This method is used to diagnose various kidney diseases and issues without invasive procedures.
Main purposes of kidney USG:
- Assess kidney structure (size, shape, position)
- Detect anomalies (stones, cysts, tumors)
- Evaluate blood flow using Doppler USG
- Monitor kidney function in patients with chronic conditions
USG is often the first choice for examining suspected kidney problems.
Procedure
Before the procedure, patients are usually advised to arrive with a full bladder, drinking 0.5–1 liter of water about an hour prior. A full bladder improves visualization of the kidneys and surrounding structures.
Special dietary restrictions are usually not required, but in some cases, doctors may advise avoiding carbonated drinks or foods that cause gas.
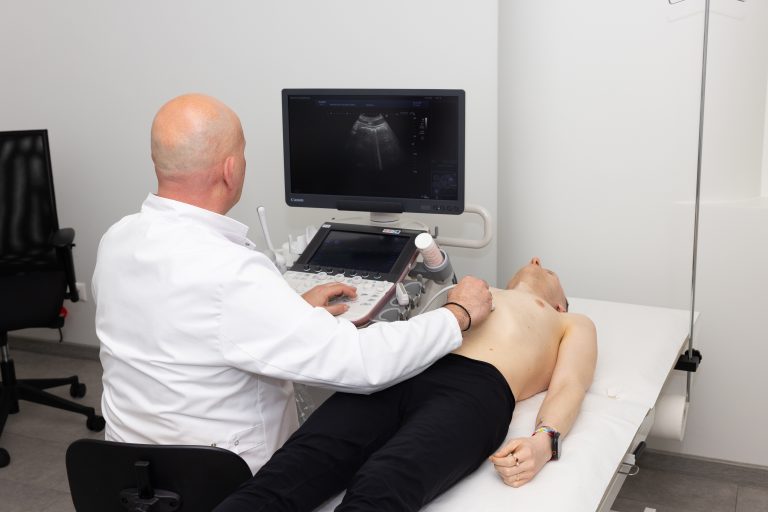
During the procedure, the patient usually lies on their back or side. A gel is applied to the abdomen to improve ultrasound conduction. The specialist moves the probe over the kidney area, sending high-frequency sound waves that reflect off tissues to create images on the monitor.
During the examination, the doctor may ask the patient to:
- Hold their breath briefly
- Change body position
- Breathe deeply or exhale
After the procedure, the doctor analyzes the images, evaluating kidney size, shape, and structure. Modern USG devices can detect even small pathologies, such as tiny stones or small cysts.
Bladder ultrasound (USG)
Bladder ultrasound is a safe and painless diagnostic method that allows doctors to assess the bladder’s condition, including the walls, volume, and any potential pathologies. For optimal results, patients should arrive with a full bladder, drinking about 1 liter of water 1–2 hours before the exam.
This examination is particularly useful for diagnosing bladder problems such as inflammation, stones, or tumors.
Procedure
The patient usually lies on their back. A gel is applied to the lower abdomen for better contact between the probe and the skin. The specialist moves the probe over the bladder area. The probe emits sound waves that reflect off tissues and organs, creating images on the screen.
The procedure is painless and usually takes 10–15 minutes. The doctor may ask the patient to change position to improve visibility, and sometimes the exam is performed first with a full bladder and then after emptying it.
Frequently asked questions
When is kidney ultrasound needed?
- Pain in the kidney or abdominal area
- Changes in urine composition or blood in urine
- Suspected kidney stones, cysts, or tumors
- High blood pressure or kidney function disorders
- Family history of kidney disease or chronic conditions affecting the kidneys
When is bladder ultrasound needed?
- Frequent urination problems
- Pain in the lower abdomen or while urinating
- Blood in the urine
- Suspected bladder stones, tumors, or inflammation
- Incomplete bladder emptying or urine retention
- Chronic urinary tract infections to evaluate complications and treatment effectiveness
Cost of ultrasound?
Kidney and bladder ultrasound at “Republikas laukuma klīnikā” in Riga is €60.00.